Breathtaking Info About Is RS232 And RS485 The Same

RS232 vs. RS485
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever wondered about the alphabet soup of communication protocols in the tech world? Two big names that often pop up are RS232 and RS485. Now, if you're thinking they're interchangeable, hold on! They're both serial communication standards, meaning they transmit data bit by bit, but that's where many of the similarities end. Think of them as being from the same family (serial communication), but having very different personalities and skill sets.
RS232, bless its heart, is the older, simpler sibling. It's been around for ages, and you might remember it from connecting older computers to peripherals like modems and mice. It's a single-ended communication standard, which basically means it uses a single wire for data transmission relative to a common ground. Think of it like shouting a message; it works okay if the listener is right next to you, but gets garbled quickly over distance.
RS485, on the other hand, is the younger, more robust sibling. It's designed for industrial environments and longer distances. It uses differential signaling, meaning it transmits data over two wires, and the difference in voltage between the wires represents the data. This is like whispering a secret using two cups and a string; the noise is cancelled out, and the message gets through clearly even over longer distances.
In a nutshell, while both RS232 and RS485 are used for serial communication, their methods of transmitting data and their intended applications differ significantly. Confusing them is like mistaking a bicycle for a motorcycle — both are vehicles, but you wouldn't take a bicycle on the highway!

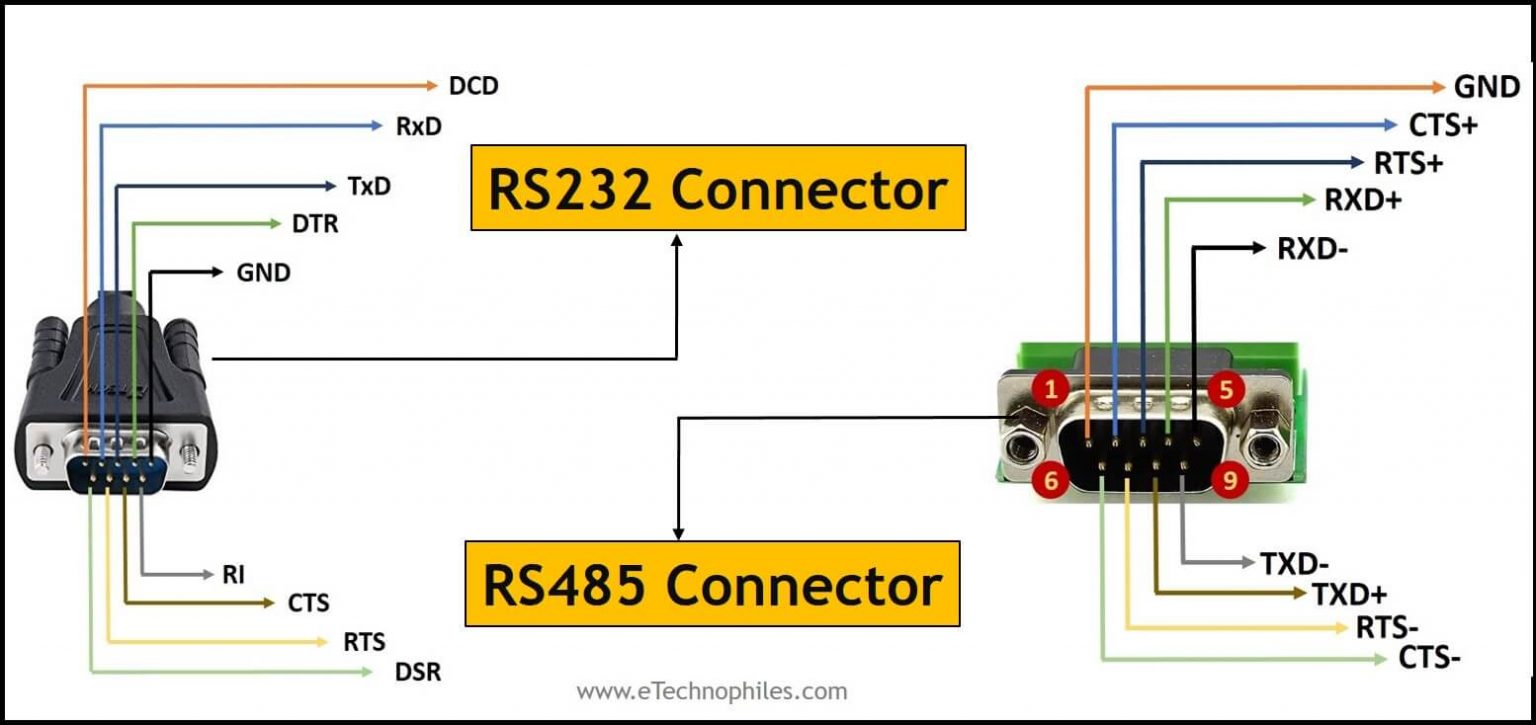
What Is The Difference Between Serial RS485 And RS232? RayMing PCB
Distance Matters
2. RS232's Short Leash
One of the biggest differences between RS232 and RS485 lies in their communication range. RS232 is notoriously short-winded. Generally, it's only reliable for distances up to about 50 feet, and even then, you might experience signal degradation. Imagine trying to have a clear conversation with someone across a football field using only your voice — it's just not going to work!
The limitation of RS232 stems from its single-ended signaling. Because the signal is referenced to ground, it's susceptible to noise and voltage drops over longer distances. This noise can corrupt the data, leading to errors and unreliable communication. In practical terms, this means that RS232 is best suited for connecting devices that are in close proximity to each other, like a computer and a printer on the same desk.
Think of RS232 as a close-range radio. It's great for sending quick messages to nearby devices, but it's not designed for long-distance communication. Trying to push it beyond its limits is like trying to power a city with a AA battery — you're just not going to get the results you need.
So, if your application requires communication over longer distances, RS232 is generally not the right choice. Its limitations in range and noise immunity make it unsuitable for industrial environments or any situation where devices are physically separated by significant distances.
Basics Of RS232, RS422, And RS485 Serial Communication
RS485
3. Differential Signaling for the Win
RS485, on the other hand, is built for endurance. Thanks to its differential signaling, it can reliably transmit data over distances of up to 4,000 feet (around 1200 meters). That's nearly 80 times the range of RS232! Imagine being able to whisper across a football field and still be heard clearly — that's the power of RS485.
Differential signaling works by transmitting the data as a voltage difference between two wires. This means that any noise that is induced on one wire is also induced on the other wire, and the receiver only looks at the difference between the two signals. This common-mode noise is effectively cancelled out, resulting in a much cleaner and more reliable signal, even over long distances. It's like having a built-in noise-canceling system for your data transmission.
This long-distance capability makes RS485 ideal for industrial environments, where devices are often spread out across a large factory floor or a remote monitoring site. It's commonly used in applications like industrial automation, building automation, and security systems, where reliable communication over long distances is critical.
In addition to its long-distance capabilities, RS485 also supports multi-drop configurations, meaning that multiple devices can be connected to the same communication line. This further enhances its versatility and makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications. So, if you need to send data over long distances or connect multiple devices on a single network, RS485 is the clear winner.

RS232 VS. RS422 RS485 What Is The Difference? LightOptics®
Noise Immunity
4. RS232's Vulnerability to Interference
Another key area where RS485 outperforms RS232 is in noise immunity. RS232's single-ended signaling makes it highly susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and other forms of noise. In noisy environments, this can lead to data corruption and unreliable communication. Picture trying to listen to a quiet conversation in a crowded room — the background noise makes it difficult to understand what's being said.
The problem with RS232 is that any noise that is induced on the signal wire is directly interpreted as part of the data. This is because the signal is referenced to ground, and any variation in the ground potential can also affect the signal. This makes RS232 vulnerable to ground loops and other forms of electrical interference.
In practical terms, this means that RS232 is not well-suited for industrial environments, where there is often a lot of electrical noise. It's also not ideal for applications where the communication cable runs near sources of interference, such as motors, transformers, or high-voltage power lines.
So, if you need reliable communication in a noisy environment, RS232 is generally not the best choice. Its vulnerability to interference can lead to data errors and system malfunctions. You'll need a protocol that can shrug off electrical noise like it's nothing.
RS232 VS RS485 Know The Difference
RS485
5. Differential Signaling to the Rescue
RS485, with its differential signaling, is much better equipped to handle noisy environments. Because the data is transmitted as a voltage difference between two wires, any noise that is induced on both wires is effectively canceled out. This makes RS485 highly immune to EMI and other forms of noise. Imagine having a pair of noise-canceling headphones that block out all the background noise — that's the level of noise immunity that RS485 provides.
The differential signaling in RS485 works by transmitting two signals that are equal in magnitude but opposite in polarity. The receiver then looks at the difference between the two signals. Any noise that is common to both signals is canceled out, leaving only the desired data signal. This common-mode rejection makes RS485 highly immune to ground loops, voltage spikes, and other forms of electrical interference.
This noise immunity makes RS485 ideal for industrial environments, where there is often a lot of electrical noise. It's also well-suited for applications where the communication cable runs near sources of interference. In these situations, RS485 can provide reliable communication even when other protocols would fail.
In addition to its noise immunity, RS485 also offers galvanic isolation in some implementations. Galvanic isolation provides a physical separation between the communication circuit and the connected devices, further enhancing its noise immunity and protecting against voltage surges. So, if you need robust and reliable communication in a noisy environment, RS485 is the clear choice. It's like the superhero of communication protocols, always ready to save the day from electrical interference.

Multi-Drop Capability
6. RS232's Limited Connections
When it comes to connecting multiple devices to a single communication line, RS232 falls short. Typically, RS232 supports only point-to-point communication, meaning that only two devices can communicate with each other at a time. It's like a one-on-one conversation; if someone else wants to join in, they'll have to wait their turn.
This limitation stems from the single-ended nature of RS232. Because only one device can transmit at a time, there's no mechanism for arbitrating access to the communication line. If two devices were to transmit simultaneously, their signals would collide, resulting in data corruption. This makes RS232 unsuitable for applications where multiple devices need to share the same communication channel.
In practical terms, this means that you can't simply connect multiple RS232 devices to the same communication line. You would need to use a multiplexer or some other device to switch between the different devices. This adds complexity and cost to the system.
So, if you need to connect multiple devices to a single communication line, RS232 is generally not the right choice. Its point-to-point limitation makes it unsuitable for multi-drop applications. You'll need a protocol that can handle multiple devices sharing the same communication channel without collisions or data corruption.