One Of The Best Tips About Is 24V Or 48V Better
Forklift Lithium Ion Battery 48v 60v 72v 30ah 40ah 50ah 100ah 120ah
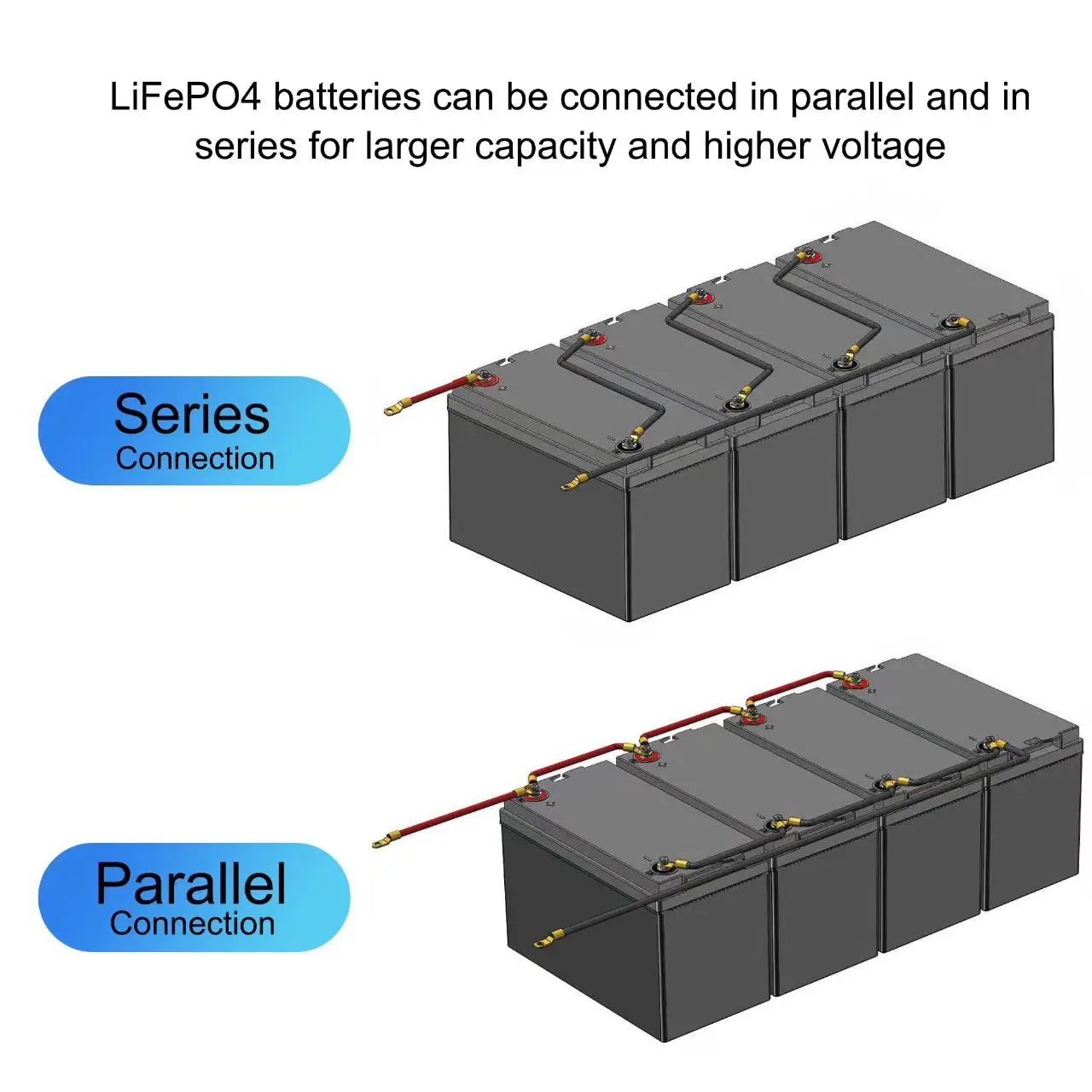
24V vs. 48V
1. The Voltage Verdict
So, you're staring down the barrel of a voltage choice: 24V or 48V? It's not exactly a decision that keeps most of us up at night, but when it comes to powering certain systems — think solar setups, electric vehicles (small ones, maybe your kid's go-kart!), or even some beefy audio amplifiers — it matters. The core question, "Is 24V or 48V better?", is definitely a worthwhile investigation. After all, nobody wants to end up with a system that sputters and dies when you actually need it. The truth is, there's no one-size-fits-all answer; it really depends on what you're trying to achieve. Let's dig in and break down the key factors.
First off, let's talk about current. Higher voltage means lower current for the same amount of power. Imagine trying to push water through a narrow pipe versus a wide pipe. High current is like the narrow pipe — lots of resistance and potential for overheating. Lower current, like the wide pipe, is more efficient and generates less heat. That's a simplified view, but it's the basic principle at play. This becomes super important when you start dealing with longer wire runs. Lower current means you can use thinner (and cheaper!) wires without significant voltage drop. Voltage drop is the enemy of efficient power transfer. If you are wondering about the cost, using thinner wire for your connection might save you some extra bucks.
Another thing to consider is safety. While neither 24V nor 48V is typically considered "high voltage" in the truly dangerous sense, 48V can pack more of a punch if you accidentally come into contact with it. It's enough to give you a noticeable jolt, while 24V is usually just a tingle. So, if you're working in an environment where there's a higher risk of accidental contact, or if you have less experience with electrical systems, 24V might be a slightly safer option. Of course, always follow proper safety precautions regardless of the voltage you're working with!
Also, component availability is worth mentioning. While both 24V and 48V components are readily available these days, you might find a wider selection of devices specifically designed for one voltage over the other, depending on your specific application. For example, in some industrial automation settings, 24V is almost a standard, so you'll have a plethora of sensors, controllers, and power supplies to choose from. For larger solar installations, 48V is becoming increasingly common because it allows for more efficient power transmission over longer distances. So, it pays to do a little research and see what's most common in your particular field.

LiFePO4 Voltage Chart (3.2V, 12V, 24V 48V) Comparison
Delving Deeper
2. Why Thicker Isn't Always Better (When It Comes to Wires)
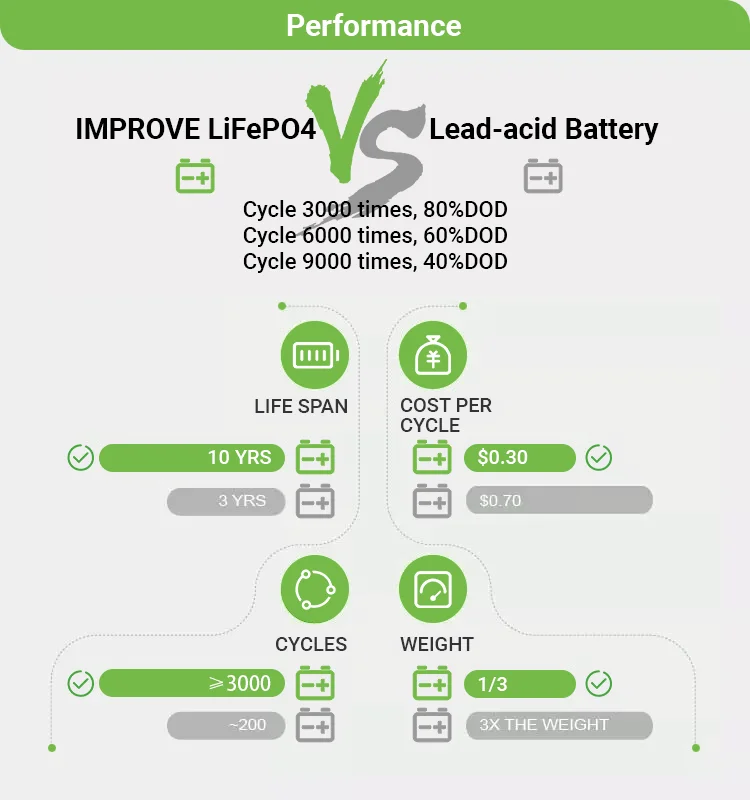
Now, let's get a little more technical. Efficiency is the name of the game. Think about it: you want as much of the power generated to actually do something useful, rather than being lost as heat due to resistance in the wiring. As mentioned earlier, higher voltage (48V in this case) allows for lower current. Lower current means less heat loss in the wires. This is especially crucial for applications with long cable runs, such as in solar power systems where the panels might be located a considerable distance from the batteries or inverters. Imagine wasting a significant portion of your solar energy just heating up the wires — not ideal!
That brings us to wire gauge. Wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wire. Thicker wires have less resistance, but they're also more expensive and harder to work with. By using a 48V system, you can often get away with using a thinner wire gauge compared to a 24V system for the same power level and distance. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially in larger installations. Plus, thinner wires are easier to bend and route, making the installation process a bit smoother. Its a win-win situation, really.
Consider also the implications for battery banks. To achieve the same total power output, a 24V system needs to deliver twice the current of a 48V system. This means the battery bank, wiring, and charge controllers need to be sized accordingly. This might result in larger, heavier, and more expensive components. With 48V, things are generally smaller, lighter, and more manageable, which is a big advantage, especially in mobile applications like RVs or boats where space is at a premium. Think of it like packing for a trip: would you rather carry two heavy suitcases or one slightly lighter one?
Let's not forget about inverters. Inverters convert DC power (like from batteries or solar panels) to AC power (like what comes out of your wall outlets). Inverters designed for 48V systems are often more efficient than those designed for 24V systems, particularly at higher power levels. This is because they can handle higher voltages with less internal loss. This is important because inverter efficiency directly impacts the overall efficiency of your system. A more efficient inverter means more of the power you generate actually gets used, rather than being wasted as heat.
Forklift Lithium Ion Battery 48v 60v 72v 30ah 40ah 50ah 100ah 120ah
Application Scenarios
3. Choosing the Right Voltage for the Job
Okay, enough with the theory. Let's get practical and look at some specific scenarios where either 24V or 48V might be the better choice. For smaller, self-contained systems, like a small off-grid cabin with a few lights and a radio, 24V might be perfectly adequate. The lower voltage is a bit safer, and the current levels are manageable with readily available components. Plus, the cost difference between 24V and 48V components might not be significant enough to justify the higher voltage.
On the other hand, for larger systems, such as a whole-house solar power system or an electric vehicle, 48V is generally the way to go. The higher voltage allows for more efficient power transfer over longer distances, reducing the need for thick, expensive wiring. It also allows for smaller, lighter components, which can be a significant advantage in mobile applications. Furthermore, many modern inverters and charge controllers are designed to operate at 48V, offering better performance and efficiency.
Consider golf carts and other small electric vehicles. Many older golf carts used 36V systems, but newer models are increasingly switching to 48V. This allows for more power and longer run times without significantly increasing the size or weight of the battery pack. The higher voltage also allows for better motor efficiency, resulting in improved performance. It's all about squeezing every last drop of performance out of the available power.
In the realm of audio amplifiers, both 24V and 48V can be found, depending on the power requirements of the amplifier. Lower-power amplifiers might use 24V, while higher-power amplifiers often use 48V or even higher voltages to deliver the necessary power to the speakers. The higher voltage allows for greater headroom and less distortion, resulting in a cleaner, more powerful sound. It's all about getting that crystal-clear audio quality, even at high volumes.

24V 48V Better Than Edison Nickel Iron Battery TN700ah For Solar
Safety First
4. A Quick Reminder on Electrical Safety
Regardless of whether you choose 24V or 48V, it's absolutely crucial to prioritize safety when working with electrical systems. Electricity can be dangerous, and it's important to take the necessary precautions to protect yourself and others. Always disconnect the power source before working on any electrical components. This might seem obvious, but it's a step that's often overlooked. Double-check that the power is off before you start tinkering around.
Use properly insulated tools and wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection. Insulated tools will help prevent accidental shocks, while gloves and eye protection will protect you from burns and flying debris. It's better to be safe than sorry. A little bit of preparation can go a long way in preventing accidents.
Never work on electrical systems when you're tired or distracted. Fatigue and lack of focus can lead to mistakes, which can have serious consequences. If you're feeling tired, take a break and come back to the project later when you're feeling refreshed. It's not worth risking your safety just to get the job done a little faster.
If you're not comfortable working with electrical systems, or if you're unsure about something, don't hesitate to seek help from a qualified electrician. It's always better to err on the side of caution. A professional electrician has the knowledge and experience to safely and correctly install or repair electrical systems. Don't be afraid to ask for help when you need it.

48V/24VDC 100W Converter Efficiency Vs. Percent Load Download
Making the Choice
5. Voltage Showdown
So, "Is 24V or 48V better?". There's no universal "winner." It really depends on your specific needs and application. Think about the size of your system, the length of your wire runs, your budget, and your safety considerations. Consider the available components and their compatibility with your chosen voltage. Taking these into account will helps you to decide what's better for you.
If you're building a small, self-contained system and safety is a major concern, 24V might be the better choice. If you're building a larger system with long wire runs and efficiency is paramount, 48V is likely the way to go. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult with a qualified electrician if you're unsure about anything.
Ultimately, the best voltage is the one that meets your specific requirements and allows you to achieve your goals safely and efficiently. Do your research, weigh the pros and cons, and make an informed decision. And don't be afraid to ask for help along the way. There are plenty of resources available to help you make the right choice.
Choosing the right voltage is like choosing the right tool for a job. A hammer might be great for driving nails, but it's not going to be very effective at cutting wood. Similarly, 24V might be perfect for some applications, while 48V is better suited for others. The key is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each voltage and choose the one that's best suited for the task at hand. Happy powering!

Difference Between 12V, 24V And 48V Solar Panel System Home Senator
FAQ
6. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is 48V inherently more dangerous than 24V?
A: While 48V can deliver a more noticeable shock, both voltages can be dangerous under the wrong circumstances. Always follow proper safety precautions when working with any electrical system. The key is to respect electricity and take the necessary steps to protect yourself.
Q: Can I mix 24V and 48V components in the same system?
A: Generally, no. Mixing different voltages can damage components and create safety hazards. Make sure all the components in your system are compatible with the same voltage. Voltage converters can be used in specific situations, but it's best to avoid mixing voltages if possible.
Q: Does a higher voltage always mean higher power?
A: Not necessarily. Power (measured in watts) is determined by both voltage and current. You can have a low-voltage system with high current that delivers the same power as a high-voltage system with low current. The relationship is Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) x Current (Amps).
Q: Is it difficult to convert a 24V system to a 48V system?
A: Depending on the system it may be quite difficult. Certain components must be replaced such as batteries, inverters and any DC-DC converters. The existing wiring should be inspected to ensure that it is of the correct gauge for the increased voltage and amperage. Also, since this job will affect the whole system, you should also consider consulting with a qualified electrician to evaluate your system and make recommendations.