Brilliant Strategies Of Info About Is A BMS Charge Controller
Battery Management Systems (BMS) and Charge Controllers
1. Understanding the Core Functions
So, you're diving into the world of batteries, eh? Good for you! Whether you're tinkering with an electric vehicle, setting up a solar power system, or just curious about what makes your phone tick, understanding battery management is key. And naturally, the question arises: Is a Battery Management System (BMS) the same thing as a charge controller? The short answer is no, but stick around, and we'll unravel the intricacies and explain why. Think of it like this: a BMS and a charge controller are both important members of the battery safety squad, but they have very different jobs.
A charge controller, at its heart, is primarily concerned with one thing: regulating the voltage and current flowing into the battery during charging. It's basically the gatekeeper, preventing overcharging that could lead to damage, reduced lifespan, or, in extreme cases, even a fiery battery explosion (yikes!). Different charge controllers use different strategies. Some use PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to slowly decrease the amount of charge going into the battery as it gets closer to full, while others use MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) to optimize the power transfer from a solar panel array to your battery. Choosing the right charge controller depends on your charging source (solar, wind, AC adapter, etc.) and your battery chemistry.
Now, let's talk about the BMS. A BMS has a much broader role. It's not just about charging; it's about the overall health and safety of the battery pack. It's the battery's personal bodyguard, constantly monitoring everything from cell voltages and temperatures to charge and discharge currents. A BMS will kick in to protect the battery from a whole range of problems like overcharging, over-discharging, over-current, short circuits, and even excessive temperatures. It is way more complex than a charge controller.
In a nutshell, think of the charge controller as managing the input to the battery, ensuring it charges safely, while the BMS manages the overall health and safety of the battery, protecting it from a wider range of potential problems during both charging and discharging. They are separate entities that work together to keep everything running smoothly and safely.

Bms Means In Electrical At Warren Caldwell Blog
Charge Controllers
2. Delving Deeper into Charge Controller Functionality
Okay, so we've established that charge controllers are the guardians of the charging process. But what does that actually mean? Let's break it down a bit further. Imagine trying to fill a glass of water without looking. You'd probably overfill it and make a mess, right? That's what would happen to your battery without a charge controller! It would just keep accepting current until it's bloated, unhappy, and potentially dangerous. No one wants that!
Charge controllers primarily focus on regulating the voltage and current coming from the charging source. If you're using solar panels, for example, the voltage and current can fluctuate wildly depending on the amount of sunlight. The charge controller smooths out those fluctuations and delivers a stable, safe charging current to the battery. It also prevents back-flow of current from the battery to the solar panel at night, which can drain your battery. Think of it as a one-way valve that ensures energy only flows in the right direction.
There are different types of charge controllers, and the best one for you depends on your specific needs. PWM charge controllers are simpler and more affordable, making them a good choice for smaller systems. MPPT charge controllers, on the other hand, are more sophisticated and can squeeze more power out of your solar panels, especially in less-than-ideal conditions (like cloudy days). They do this by constantly adjusting the voltage and current to find the "maximum power point" of the solar panel array. Like a GPS device, MPPT charge controllers are more sensitive, and find more precise location.
Choosing the right charge controller is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of your battery. Its about knowing your solar system design, panel types, location conditions, and battery chemistry to make informed decisions. Also consider protection feature to avoid overcharging the battery, so you are safe.

BMS
3. Exploring the Many Facets of Battery Protection
Now, let's shift our attention to the Battery Management System (BMS). Imagine you're a doctor, and the battery pack is your patient. You wouldn't just check their temperature, right? You'd want to check their blood pressure, heart rate, cholesterol levels, and a whole bunch of other things to get a complete picture of their health. That's essentially what a BMS does for your battery.
A BMS constantly monitors a whole host of parameters, including individual cell voltages, temperature, current, and state of charge (SOC). It uses this information to protect the battery from damage and optimize its performance. For example, if one cell in the battery pack starts to get too hot, the BMS can reduce the charging or discharging current to prevent it from overheating. If a cell voltage drops too low during discharge, the BMS can disconnect the load to prevent over-discharge, which can permanently damage the cell. Its main job is to optimize and protect.
Furthermore, a BMS often includes cell balancing functionality. In a battery pack made up of multiple cells in series, it's common for the cells to become slightly unbalanced over time. This means that some cells may have a higher voltage or lower capacity than others. The BMS can redistribute charge between the cells to keep them balanced, which improves the overall capacity and lifespan of the battery pack. Cell balancing ensures that the entire battery pack is used efficiently and helps prevent premature failure of individual cells. A healthy and balance battery is essential.
Think of the BMS as the brains of the battery system. It's constantly gathering information, making decisions, and taking actions to ensure that the battery operates safely and efficiently. Without a BMS, your battery pack would be much more vulnerable to damage and premature failure, especially in high-performance applications like electric vehicles.
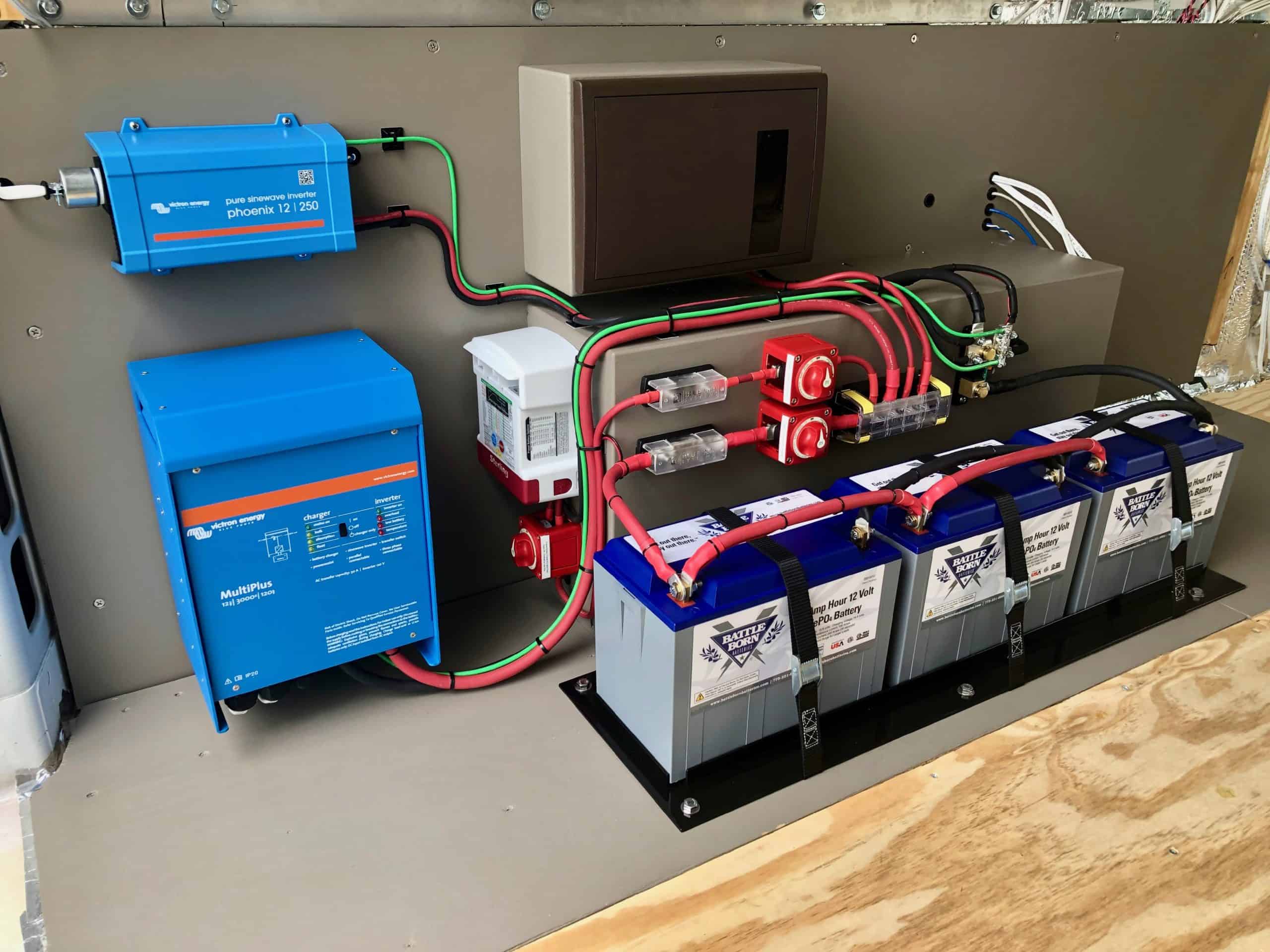

Key Differences Summarized
4. Distinguishing Roles for Optimal Battery Health
Lets nail down the key differences between a BMS and a charge controller. It's all about distinct roles contributing to the overall battery health, just like different members of a team with specialized skills.
Firstly, a charge controller solely focuses on the charging process. Its job is to manage the input of energy into the battery. By contrast, a BMS is concerned with the entire operation of the battery, including charging, discharging, and everything in between. Think of the BMS as a holistic manager, ensuring all aspects of battery health are maintained.
Secondly, consider the parameters they monitor. A charge controller primarily tracks voltage and current during charging. A BMS, however, monitors a much broader range of parameters, including cell voltages, temperature, current, and state of charge (SOC). This comprehensive monitoring enables the BMS to provide a more nuanced and complete protection strategy for the battery.
Finally, the scope of protection differs significantly. A charge controller primarily protects against overcharging. A BMS protects against a wide range of issues, including overcharging, over-discharging, over-current, short circuits, and excessive temperatures. The BMS acts as the batterys first line of defense against a variety of potential threats, making it a more versatile protection system.
What Is A Battery Management System? BMS Building Blocks, Working
The Power Couple
5. Ensuring Battery Longevity and Safety
While a BMS and a charge controller are distinct devices with separate functions, they often work together to provide comprehensive battery protection. It's like having a security system with both a guard at the gate (charge controller) and internal surveillance cameras (BMS) ensuring complete protection. This synergistic relationship ensures both longevity and safety.
Imagine a solar power system. The charge controller regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery, preventing overcharging. Meanwhile, the BMS monitors the battery's temperature and voltage, ensuring that it's operating within safe limits. If the BMS detects a problem, such as an over-temperature condition, it can signal the charge controller to reduce or stop charging, further protecting the battery. Their combined efforts prevent damage.
In high-performance applications like electric vehicles, the collaboration between the BMS and charge controller is even more critical. The BMS manages the complex charging and discharging cycles, while the charge controller ensures that the battery is charged safely and efficiently. They are an interconnected set of protection, safety and optimization.
So, can a BMS replace a charge controller? Technically, some advanced BMS systems might incorporate basic charge control features. However, it's generally best to use both a dedicated charge controller and a BMS to provide the most robust and reliable protection for your battery system. Think of it as belt and suspenders — extra assurance is always a good idea.
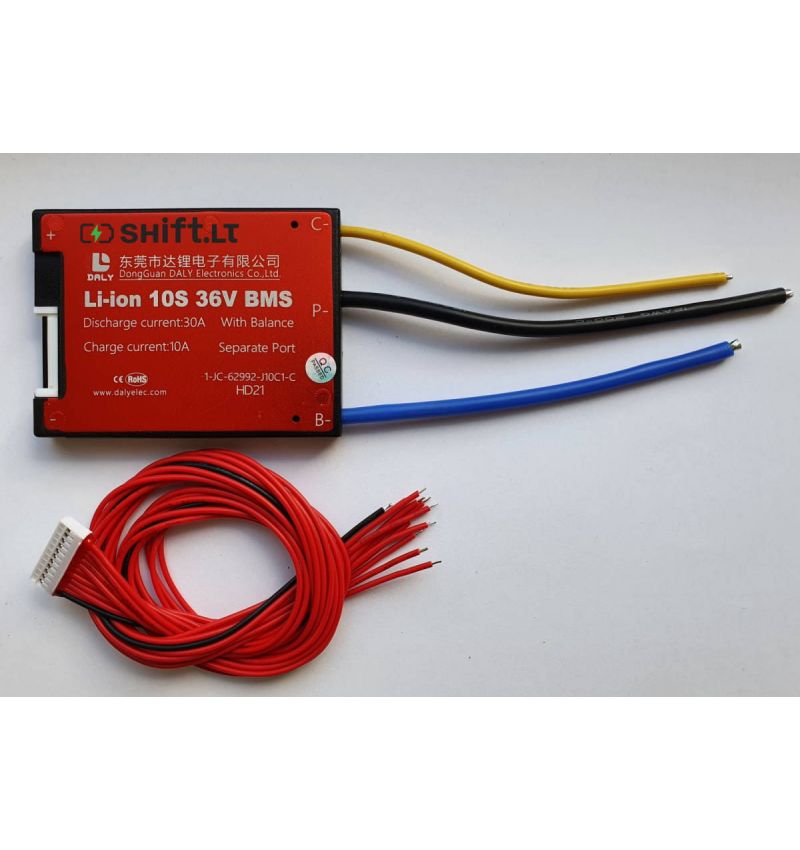

FAQ
6. Clearing Up Common Confusions
Still scratching your head? Here are some frequently asked questions to help clear up any lingering confusion.
Q: Can I use a BMS instead of a charge controller for my solar panel setup?A: While some advanced BMS units might offer basic charge control, it's generally not recommended. A dedicated charge controller is specifically designed to handle the fluctuating voltage and current from solar panels and prevent overcharging, a task that a standard BMS isn't always equipped to handle effectively. Think of it as using a wrench instead of a proper socket wrench — it might work in a pinch, but it's not the best tool for the job.
Q: What happens if I overcharge my lithium-ion battery?A: Overcharging a lithium-ion battery can be dangerous. It can lead to reduced lifespan, swelling, overheating, and, in extreme cases, even fire or explosion. That's why it's so important to have both a charge controller and a BMS to prevent overcharging.
Q: Do all battery types require a BMS?A: While not every battery type absolutely requires a BMS, lithium-ion batteries especially benefit from one due to their sensitivity to overcharging, over-discharging, and temperature extremes. Lead-acid batteries, for example, are more forgiving, but a BMS can still help extend their lifespan and improve their performance. Basically, a BMS is always a good investment, regardless of the battery chemistry.
Q: How do I choose the right BMS for my battery pack?A: Selecting the right BMS depends on several factors, including the battery voltage, current capacity, and cell chemistry. You'll need to ensure that the BMS is compatible with your battery's specifications and that it can handle the maximum charging and discharging currents. It's always a good idea to consult with a battery expert or refer to the battery manufacturer's recommendations to ensure you choose the right BMS for your needs. And remember, when in doubt, go for a slightly more capable BMS — it's better to have more protection than not enough!